ABS is one of the most widely used 3D printer filaments, mainly due to the very good material properties.
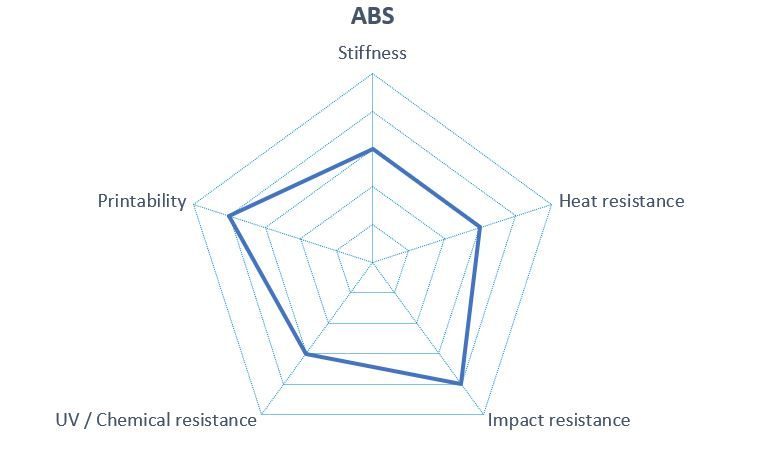
ABS has many advantages that make the filament universally usable. The most important properties of this material are high stiffness and toughness. It is a robust material with excellent scratch and impact resistance, which means that the 3D objects pressed from ABS will not break so quickly if they fall on the floor. ABS is characterized with good heat resistance, as the melting point is over 100° C. Models printed with ABS have a light weight and are slightly flexible. Post-processing of ABS 3D objects also proves easy, due to its relatively soft surface hardness.
These properties make it useful for prototypes, housings, toys, body parts, brackets, safety helmets and more.
Due to its temperature properties, ABS has a tendency to warp, i.e. the corners and edges can detach from the print bed and warp during the printing process.
ABS has low UV resistance, which means that the 3D-printed part becomes brittle and quickly turns yellow when exposed to UV light for a long time.
In addition, ABS is not considered environmentally friendly because it cannot be biodegraded. This means, the material cannot be used for 3D printing for food storage.
Advantages
Disadvantages
ASA is considered the “outdoor” alternative to ABS due to its higher resistance to heat, UV radiation, moisture and many chemicals. The 3D objects made with ASA can survive extreme weather conditions without affecting color and shape.
As a filament, ASA impresses with its very good impact resistance. High strength and stability are further convincing points that speak for this material.
3D components printed with ASA have a high-quality glossy surface. In addition, components made of ASA can be post-processed very easily: milling, sawing, drilling, grinding, gluing, painting are all possible to bring 3D printing to the desired end result.
Due to the thermal properties of the material tend 3D ASA parts to warp. In addition, the ASA filament is susceptible to certain organic compounds. If the filament comes into contact with esters, ketones and ethers, stress cracking could occur on the surface.
As a filament, ASA is ideal for outdoor applications, such as decorations for the garden, as well as various outdoor applications in the automotive industry or prototypes. The material is also well suited for electronic items and tools, as well as housings. It could be used also for common objects, for which a hard surface is not necessary.
Advantages
Diasadvantages
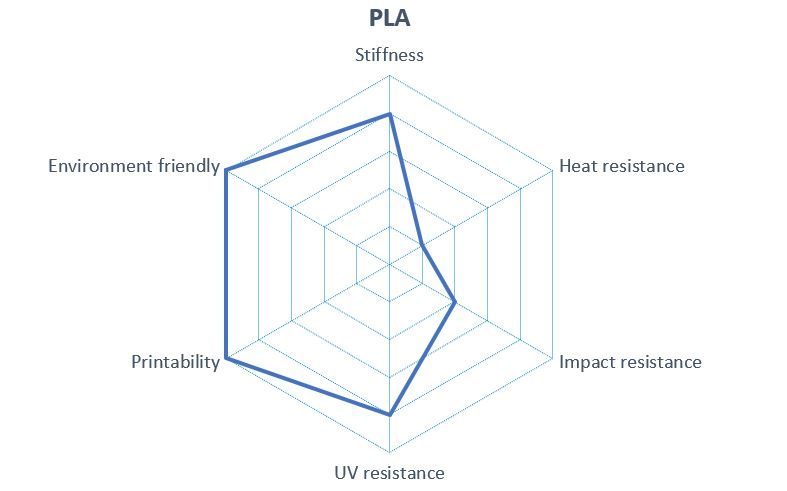
PLA is an easy-to-use filament that can be used to make almost any 3D print. PLA is made from renewable raw materials and is biodegradable. This makes the plastic a biocompatible and food safe. On the other hand, the material is not suitable for thermally intensive applications as the melting temperature is about 65 °C. Overall, this material has good mechanical properties, especially high stiffness. A major advantage of this filament is the fact that the warping risk is very low, which speaks for the good printability and quality of this material. In addition, PLA has a high UV resistance. PLA tends to absorb water, which means that PLA-3D objects can become over time brittle or fragile. Post-processing of PLA 3D objects is limited due to its moderate impact resistance.
This filament is a good choice for 3D printing decorative objects, architectural models and figures. Due to its biocompatibility, it is suitable for food packaging, toys as well as medical applications.
Advantages
Disadvantages
TPU filaments have similar properties to vulcanised rubber, also known as caoutchouc. It is a very flexible and elastic material, which makes TPU unique. Its rubber-like elasticity in combination with its enormous durability make the filament very interesting for numerous applications in different industries. It is often used for example in the sports sector, as it is perfectly suited for the production of protectors, fitness equipment and wristbands. With its elastic properties and pliant surface is TPU even interesting for the production of shoe soles and mobile phone covers.
Furthermore, TPU is characterised by its weather and UV resistance, as well as excellent resistance to many chemical substances, oils and greases. In addition, TPU absorbs shocks well, which is advantageous for the manufacture of applications for damping mechanical vibrations, cushioning elements, seals and flexible joints. TPU is perfect for objects that need to bend yet do not break, and also have good durability. TPU is unfortunately not food safe, but it is environmentally friendly and can be biodegraded. The material shows little tendency to warp, but printing with this material requires knowledge.
Advantages
Disadvantages
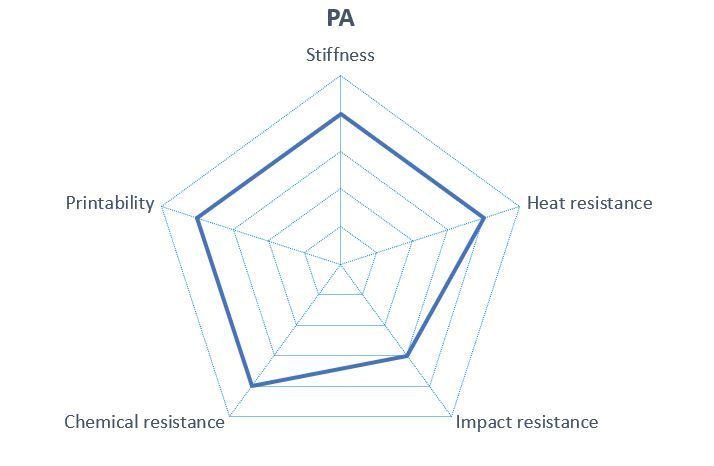
Working with nylon requires good experience, because despite its very good physical properties, the filament shows severe distortion when cooling.
Otherwise, the completely synthetic material can be used for many applications. Very good stability, high heat resistance, and high resistance to chemicals are some advantages of nylon. The material is also weather resistant. This is a property that makes the nylon 3D models very durable and long-lasting. Another plus is the high impact resistance, which makes the parts printed with nylon almost unbreakable. The nylon 3D models are very robust and have a very low coefficient of friction, so they are ideal for mechanical load-bearing parts, for example.
Like all polyamides, nylon tends to absorb moisture when unprocessed, causing the filament to swell. The tendency to warp could lead to poor 3D prints if you have little experience with the material. In addition, nylon tends to string during printing. It already soaks up water during printing, which can have a negative impact on the stability and quality of the 3D object. Overall, nylon is one of the most difficult materials to print.
Nylon is used in numerous applications, such as load-bearing objects like gears and gear chains, hinges, fittings. Just as well, nylon can be used to make various brackets, household items, toys and containers.
Advantages
Disadvantages
PA12CF is a filament based on polyamide 12 (PA12). The material is reinforced with carbon fibres to improve its properties. For example, PA12CF features better heat resistance and a lower shrinkage ratio compared to PA12. In addition, the carbon fibres improve the stiffness and the impact resistance. Another plus is the fact that the weight is reduced due to the carbon fibres.
All these advantages make the filament interesting for many functional and demanding applications, including prototypes, tools and final components, various mechanical parts with high durability.
Advantages
Disadvantages
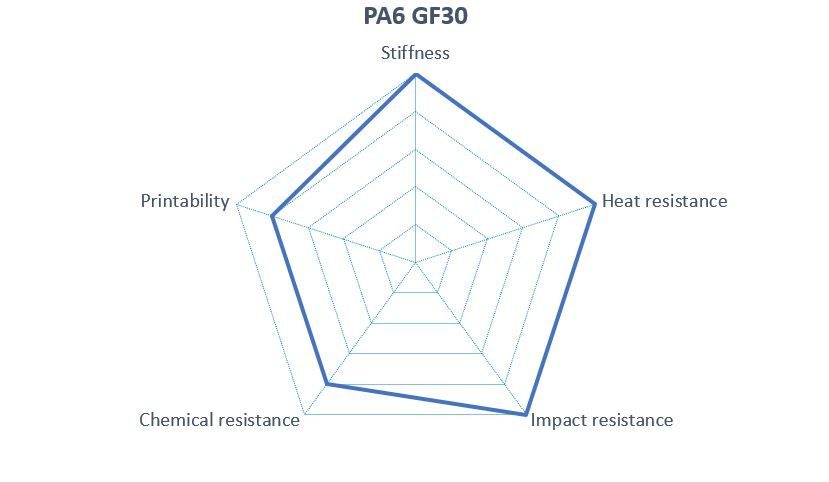
Is a polyamide reinforced with 30 % glass fibres. As a result, PA6 GF30 is characterised by high strength and stiffness. In addition, the filament has very good heat, creep and dimensional stability. These characteristics make the material suitable for printing parts with high dynamic and static loads that have to withstand high temperature conditions over time. The filament is used in numerous applications in the mechanical engineering and automotive industries, as well as conveyor and transport technology, e.g. gear wheels and racks, seals, brackets, guide parts. These have a very good strength-to-weight ratio.
The material also has other advantages. It is resistant to many oils, greases and fuels and for this reason it is easy to bond. Additionally, the material is wear-resistant and has good machinability, which enables good post-processing of parts printed with it. Such parts have low shrinkage and warpage, and moisture absorption is also low. The surface is rougher compared to non-reinforced plastics, but has a higher dimensional stability.
The glass fibres lead to an abrasive effect of the surface. For this reason, this material is rather unsuitable for sliding guides.